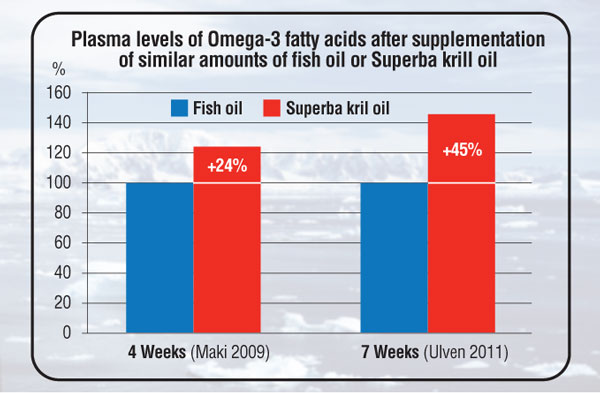
Percentage increase of plasma EPA and DHA after the consumption of the same amount of Omega-3 fatty acids in the form of Superba krill oil in comparison to fish oil after 4 weeks (1) or 7 weeks (2)
References
1. Maki, K. C., Reeves, M. S., Farmer, M., Griinari, M., Berge, K., Vik, H., Hubacher, R., and Rains, T. M. (2009) Krill oil supplementation increases plasma concentrations of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in overweight and obese men and women. Nutr Res 29, 609-615
2. Ulven, S. M., Kirkhus, B., Lamglait, A., Basu, S., Elind, E., Haider, T., Berge, K., Vik, H., and Pedersen, J. I. (2011) Metabolic effects of krill oil are essentially similar to those of fish oil but at lower dose of EPA and DHA, in healthy volunteers. Lipids 46, 37-46